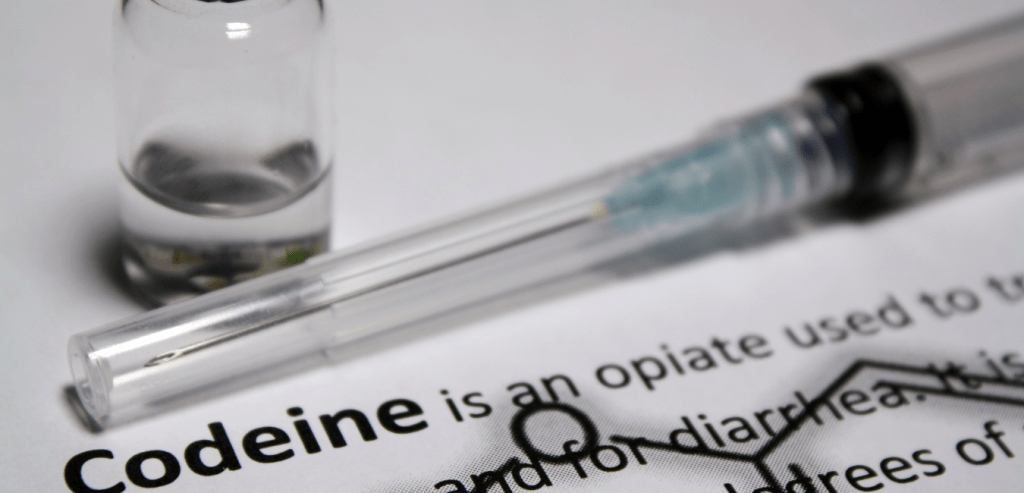
Codeine addiction is a widespread, far-reaching problem that spans across ages, ethnicities and socioeconomic backgrounds.
Codeine is an opiate drug often found in prescription-strength cough syrups, or in a combination formulation with various other analgesics (for example, with acetaminophen – under the brand name Tylenol 3). It is used clinically to treat pain and coughing; however, it is also often abused due to its euphoric side effects.
Codeine addiction is a widespread, far-reaching problem that spans across ages, ethnicities and socioeconomic backgrounds.
Codeine is an addictive drug with potentially dangerous effects at high dosages. It essentially acts as a depressant of the central nervous system. This leads users to experience:
- Feelings of relaxation.
- Euphoria.
- Drowsiness.
- Slowed heart rate.
These effects are perceived as pleasant, and the user may become addicted to these effects and, in turn, the drug.
The addictive nature of codeine, and the physical dependency that may develop over time, can lead to difficult and unpleasant withdrawal symptoms including:
- Sweating and chills.
- Malaise.
- Extreme irritability.
- Abdominal discomfort.
- Diarrhea.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF ABUSE
If you think someone you are close to may be addicted to codeine, there are a few traits for which you can keep an eye out:
- Dizziness and staggering.
- Itchiness and scratching (often of the nose).
- Constricted or pinpoint pupils.
- Slow breathing.
- Confused mental state.
- Complaints of constipation.
- Blue appearance to lips or fingernails.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Delirium and hallucination.
- Seizures.
EFFECTS OF CODEINE ABUSE
There are many unpleasant sides of codeine abuse, some of which can be fatal. These effects include:
- Gastrointestinal distress.
- Clouded thinking and impaired judgment.
- Depression.
- Drastic lowering of blood pressure.
- Slowed heart rate.
- Liver malfunction (especially with the Tylenol formulations).
Markedly lowered heart and respiration rates can result from central nervous system depression. The resulting decrease in oxygenated blood to the brain and other vital organs can lead to seizures or even death.
Credited to: Drug Abuse