Cocaine is a powerfully addicting drug of abuse that directly affects the brain. The pure chemical, cocaine hydrochloride has been abused for over 100 years, in fact, coca leaves (the source of cocaine) have been consumed for 1000’s of years. Cocaine is considered a class II drug which means that it has high potential for abuse, but is allowed to be prescribed and administered by a doctor for medical purposes.
Chemical Structure
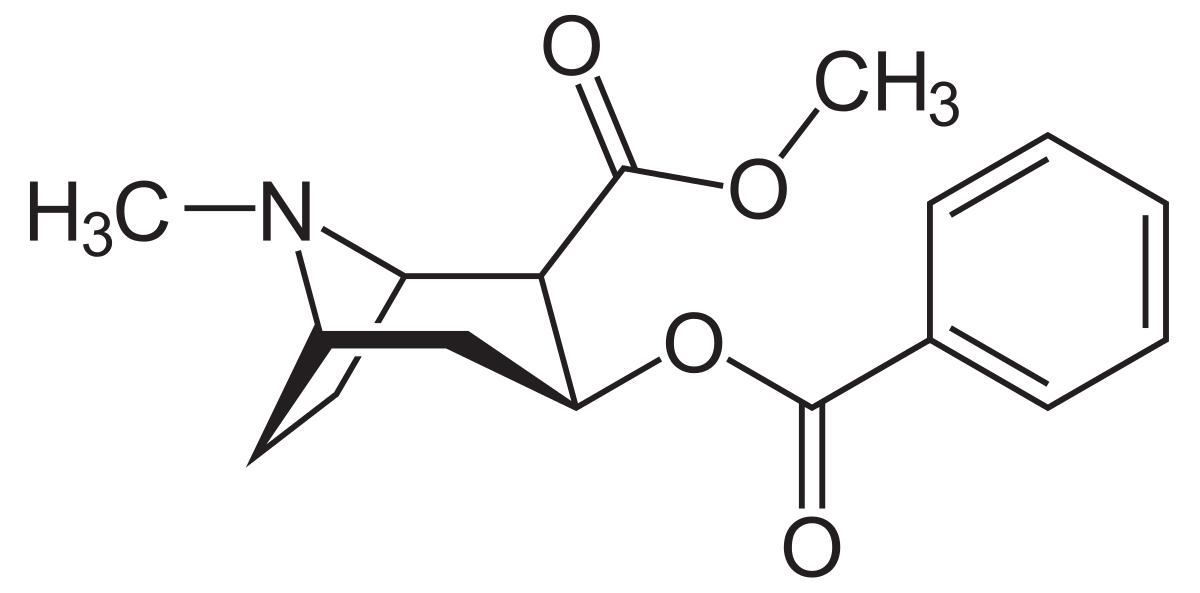
There are two chemical forms of cocaine, the hydrochloride salt and what is called the “freebase.” Cocaine hydrochloride is in a powder form and is able to dissolve in water. It is this form that can be intravenously or intranasal. Freebase cocaine has not been neutralized by acid to form the salt. It is this form that is smokable.
What is crack cocaine?

Crack refers to cocaine when the freebase form has been neutralized with acid forming the powdered cocaine hydrochloride, and has then been formed into a smokable substance, through treatment with ammonia or sodium bicarbonate and water, followed by heat to remove the hydrochloride.
Statistics of Cocaine Use in the United States*
How is cocaine consumed?

*The principal routes of cocaine administration are:
- oral (“chewing”)
- intranasal (“snorting”)
- intravenous (“mainlining”, “injection”)
- inhalation (“smoking”)
*How does cocaine produce its effects?
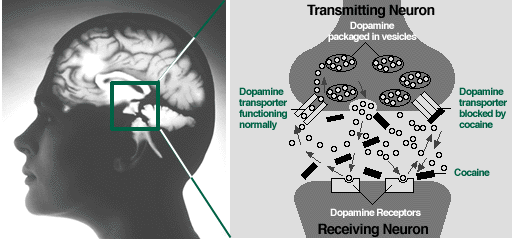
Like many other drugs, cocaine also affects the ventral tegmental area (VTA). Normally, dopamine is released by a neuron into the synapse where it binds to dopamine receptors on the neighbouring neurons. Usually, dopamine is then recycled back into the transmitting neuron by a dopamine receptor. If cocaine is present, it will attach to the dopamine receptor and blocks the reuptake of dopamine. A build-up of dopamine in the synapse contributes to the euphoric effects of cocaine.
Short term effects of cocaine use
- Effects appear almost immediately after a single dose and disappear within a few minutes or hours.
- Feelings of euphoria, energy
- Talkative
- Mentally alert, especially to the sensations of sight, sound, and touch
- Decreased appetite
- Increased heart rate and blood pressure
- Constricted blood vessels
- Increased temperature
- Dilated pupils
- Large amounts of cocaine intensify the high, but also leads to bizarre, erratic, and violent behaviour. Tremors, vertigo, muscle twitches, paranoia may also occur with high doses
- In continual large doses, a toxic reaction resembling amphetamine poisoning.
Long-term effects of cocaine use
- Addiction
- Irritability and mood disturbances
- Restlessness
- Paranoia
- Auditory hallucinations
- Tolerance to cocaine’s high – leads to increase in doses to intensify and prolong the euphoric effects.
- Sensitization to cocaine’s anaesthetic and convulsing effects without increasing the dose.
- Paranoid psychosis
Medical Complications of Cocaine Abuse
- Cardiovascular Effects
-
- disturbances in heart rhythm
- heart attacks
- Respiratory Effects
-
- chest pain
- respiratory failure
- Neurological Effects
-
- strokes
- seizures and headaches
- Gastrointestinal complications
-
- abdominal pain
- nausea